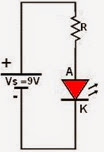
Simplest Electronics circuit
Hi guys, here is the simplest circuit; it is consisted of a resistor, an
LED, and a battery.
Calculation is given below.
Vs: 9Vdc.
Voltage to the LED, let’s say 3Vdc,
Current through LED 20mA.
Through resistor voltage to be dropped: 9-3=6 Vdc.
Current through resistor: 20mA.
Resistor: V/I=6/20= 300 Ohm.
This is very simple circuit, can be easily assembled. So try it.
Normally is very simple for hobbyist and experienced circuit makers, but
it can be a fun for new electronics hobbyist.
Collect the following components
One LED, 5mm size, one resistor of 300 Ohm, one 9V battery, and other
tools like soldering iron, cutter, wire etc.
1- Connect resistor one end to the longer pin of LED with the help of
solder (you can also connect them by twisting both the pins), Now we have two
pins spare, one pin of resistor and another one is leg of LED.
2- Now connect the resistor spare end to the positive of battery and
LED's to the negative of the battery. Now what do you see?
Is it glowing?
Yes?
So we have glowing LED now,
but the question is, we choose the resistor of 300 Ohm, why?
So we calculate the value.
3- There is a simple and most significant formula, Ohm's Law.
According to Ohm's law
I = V/R,
R=V/I,
V= I*R
I= Current (A) (current flowing through the resistor),
V= Voltage (V) (voltage across the resistor),
R= Resistance (Ohm).
In our circuit, we know…
The voltage supply voltage (Vs) = 9V.
Voltage across LED = 3V. (Normally LED 5mm runs on 3V).
Voltage dropped by resistance= 9-3=6V.
Current to be flowed through LED = 20mA = 0.020 Amp.
Resistance=?
Resistance= V/I = 6/0.020 = 300 Ohm.
NOTE: Dear friends I didn't have 330 Ohm at the time, so I used 470 Ohm.
You can control the brightness of LED by controlling the resistance value;
Resistance is to limit the current,
Resistance is to limit the current,
Warning
If you don't connect any resistance in series then current will be
infinite and LED will be burnt immediately, So enjoy the circuit.