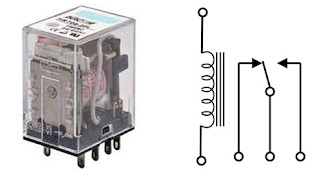
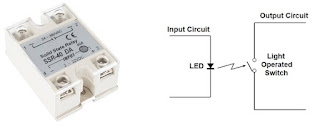
Relay is an electrically operated switch that opens
and closes the circuit by receiving electrical signal from the outside
source
Relay
Type:
Ø Relay technology is divided into two
categories
1.
Movable Contacts
2.
No-Movable Contacts
Mechanical Relay
Solid State Relay
Relay
Types:
Mechanical Relay
Ø This
relay has contacts that are mechanically actuated to open/close by a magnetic
force
Ø This
magnetic force is produced by a coil which is excited by the electric current
Ø Due to
movable part it creates noise during operation
Solid-State
Relay
Ø This
relay does not have mechanical contacts to control outputs
Ø There
are electrical switching elements such as Triac and MOSFET
Ø Since no
movable part is there so no noise it creates
Mechanical
Relay- Advantages
Ø It
provides physical isolation between input and output
Ø It can
withstand higher voltages
Ø These
relays can tolerate short-term overload condition
Ø Transients
do not affect output of the relay significantly
Mechanical
Relay- Disadvantages
Ø Due to
mechanical contacts its switching speed is slow
Ø It has
limited life span due to mechanical parts
Ø These
relays create contact-bounces which cause arcing
Solid
State Relay - Advantages
Ø It also
provides physical isolation between input and output
Ø Switching
time is less as compared to the mechanical relay
Ø Life
expectancy is higher
Ø These
Relays offer greater reliability
Ø No
contact-bounce problems
Solid
State Relay – Disadvantages
Ø Resistance
in the output circuit is normally higher as compared to an Electromechanical
relay
Ø It is
not resilient to transient spikes and other overload conditions, like a
mechanical relay, unless it is protected
Ø A transient
above the limits of the output device could destroy the solid state relay